Light with Every Step: Anchit Rai Opens a New Path for Energy Harvesting through Piezoelectric Technology
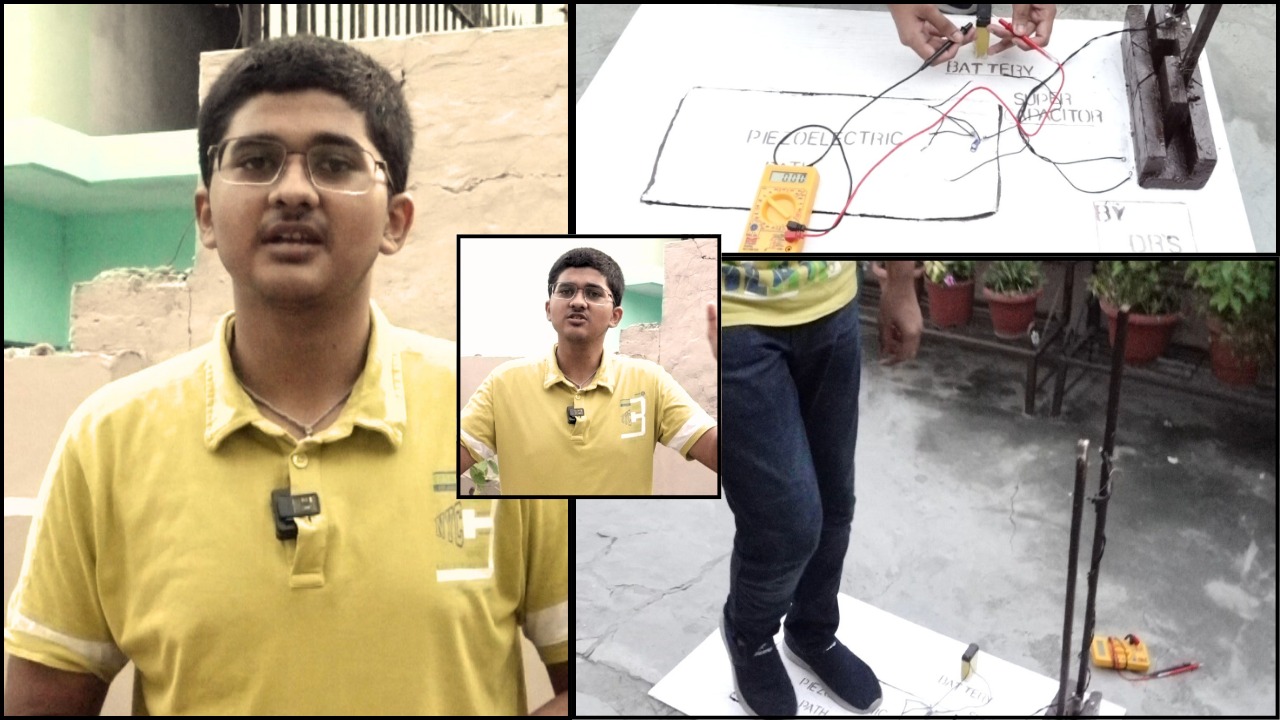
Hoshiarpur- Anchit Rai, an eighth-grade student at Mount Carmel School, Hoshiarpur, has developed a project that can convert the pressure underfoot into electricity. This project has been developed at a model level so far, but plans are now being made to implement it on a larger scale.
Hoshiarpur- Anchit Rai, an eighth-grade student at Mount Carmel School, Hoshiarpur, has developed a project that can convert the pressure underfoot into electricity. This project has been developed at a model level so far, but plans are now being made to implement it on a larger scale.
Anchit’s project is based on piezoelectric sensors, which convert the pressure exerted underfoot while walking into energy. These sensors are placed beneath tiles so that when pressure is applied by walking on them, electricity is generated. The generated electricity is stored in batteries and used for lighting at night.
The inspiration for this technology came to him during a visit to Green View Park, Hoshiarpur, where he observed that some lights were powered by electricity and others by solar energy. He thought that if electricity could be generated from human activity, it would be a remarkably efficient solution.
Each step generates approximately 2 to 5 joules of energy, which can be beneficial for providing a continuous electricity supply in crowded places such as metro stations, shopping malls, schools, or government buildings. The sensors are designed to be waterproof, durable, and capable of functioning well under slip-resistant tiles.
According to him, this technology is not only helpful in the direction of energy conservation but also in environmental protection and raising awareness among the general public. This method of electricity generation is completely free from coal or other conventional fuels and is pollution-free.
His goal is to implement this technology in more places so that clean, affordable, and sustainable energy can be available at all levels. This method can contribute to both energy conservation and environmental protection in smart cities, government buildings, schools, and other crowded areas.